Matura: Softwareentwicklung & Informationssysteme
1.1. C-Grundlagen
Grundsätzlich
- Kompakte, strukturierte, typisierte, hardwarenahe, portable, höhere Programmiersprache
- Ein-/Ausgabe ist nicht im Befehlsumfang enthalten -> Funktionen der Standardbibliothek
- Ein Zeiger repräsentiert eine Adresse und nicht wie eine Variable einen Wert. Will man auf den Wert der Adresse zugreifen, auf die ein Zeiger zeigt, muss * vor den Namen gesetzt werden.
- (Software)Bibliotheken werden mit #include <…> hinzugefügt
- Stringoperationen mit
#include <string.h>- Aufrufbar mit str…
- Bsp:
- Kopieren:
int strcpy(char * restrict ziel, const char * restrict quelle); - Vergleichen:
int strcmp(const char *str1, const char *str2); - Anhängen:
char *strcat(char * restrict str1, const char * restrict str2); - Länge:
size_t strlen(const char *str); - Zeichen suchen:
char *strchr(const char *str, int zeichen); - String suchen:
char *strstr(const char *str, const char *such_str);
- Kopieren:
int zahl = 7;
int *zeiger;
zeiger = &zahl;
printf("Zeiger-Wert: %d\n", *zeiger);
Quellcode-Übersetzen-Syntax-Semantik
- C-Quellcode muss Grammatik (Syntax) & fachliche Anforderung (Semantik) erfüllen
- Semikolon am Ende & Kommentare wie in Java
- Geschriebener Quellcode wird vom Compiler in Objektcode übersetzt und danach vom Linker mit Bibliotheken zu einem ausführbaren Programm gebunden
- Der Compiler ruft vor der eigentlichen Übersetzung den Präprozessor auf, der die Präprozessordirektive (Ganz oben #define, #include, usw.) auswertet
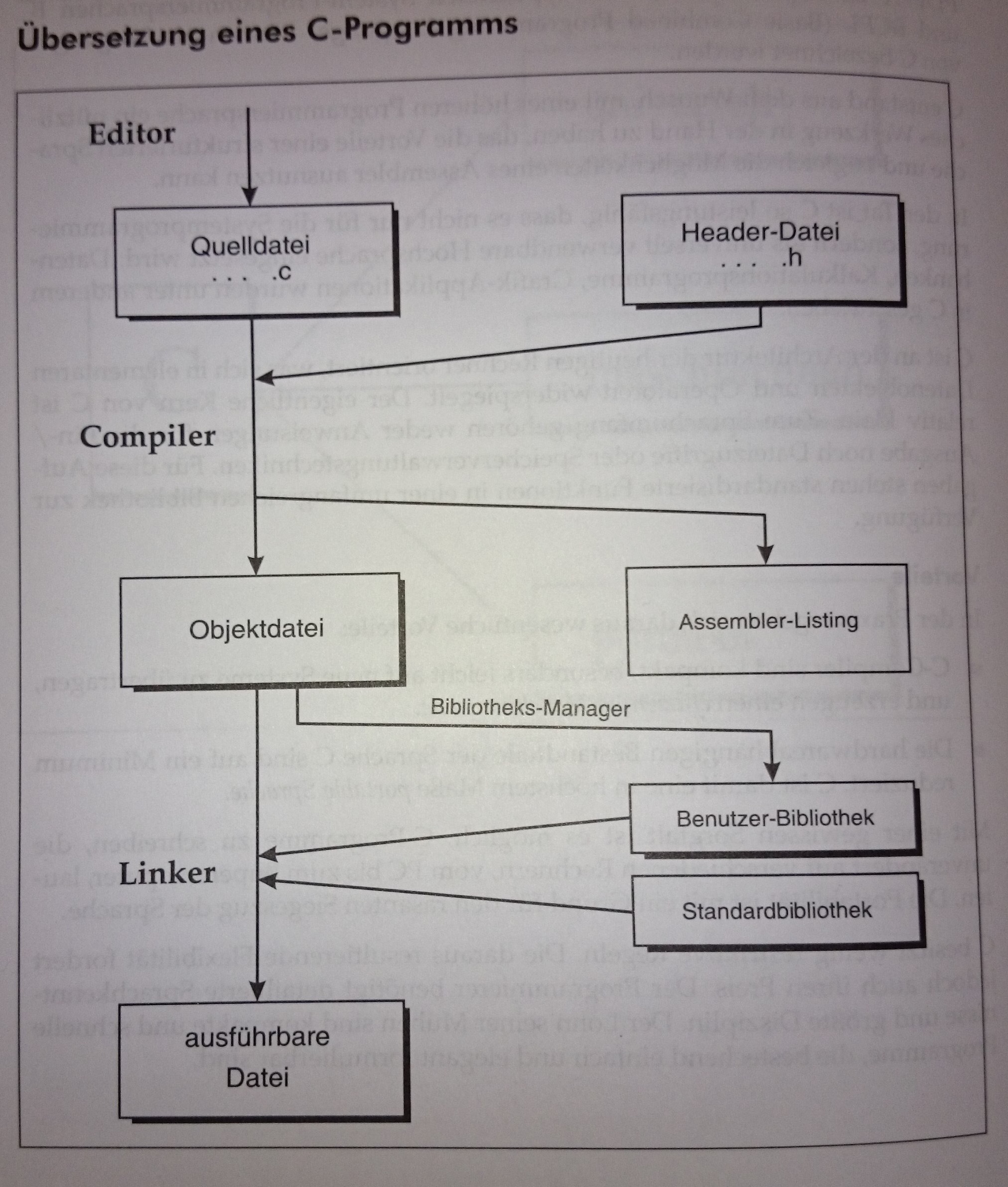
H&C-File
- C-Quellcode setzt sich aus Quellcode-Dateien (
.c) zusammen, die Header-Dateien mittels#includeeinbinden (.h); .c-File: SourceCode.h-File: Funktionsdeklarationen/Prototypen, Konstanten, usw., die in mehreren.c-Files verwendet werden
Primitive Datentypen (Datentyplänge, Unsigned/Signed)
| Type | Size (bytes) | Format Specifier |
|---|---|---|
| int | at least 2, usually 4 | %d, %i |
| char | 1 | %c |
| float | 4 | %f |
| double | 8 | %lf |
| short int | 2 usually | %hd |
| unsigned int | at least 2, usually 4 | %u |
| long int | at least 4, usually 8 | %ld, %li |
| long long int | at least 8 | %lld, %lli |
| unsigned long int | at least 4 | %lu |
| unsigned long long int | at least 8 | %llu |
| signed char | 1 | %c |
| unsigned char | 1 | %c |
| long double | at least 10, usually 12 or 16 | %Lf |
- Mit
sizeof(variable)erhält man die Größe eines Datentyps in Byte - char ≤ short int ≤ int ≤ long int ≤ long long int
- float, double & long double sind immer signed
- signed: positiv & negativ -> Wertebereich 50% pos, 50% neg
- Bsp: signed char von -127 bis 127
- unsigned: nur positiv -> Wertebereich 100% pos
- Bsp: unsigned char von 0 bis 256
Variablen-, Konstanten & Funktionen
- Buchstaben (ausgenommen Umlaute, ß), Ziffern und Unterstrich
- Mit Buchstaben beginnen
- Konstanten mit
#define NAME Wert
Ein-/Ausgabe
- Erfordert
#include <stdio.h> - Formatierung mit
sprintf(array, "Format", variablen...) - Ausgabe mit
printf("Text");oderprintf("%d", &number); - Einlesen mit
scanf("%d",&number); - Zeichenkette einlesen mit
fgets(array, laenge, stdin/File)
Prototypen
- Deklaration einer Funktion – inklusive Angaben über Anzahl, Typ der Parameter und Typ des Rückgabewertes – getrennt von ihrer Implementierung
// enthält unter anderem den Funktionsprototypen für printf():
#include <stdio.h>
// Prototypdeklaration, die Parameterbezeichner sind optional:
double summe(double zahl1, double zahl2);
int main(void) {
// Aufruf der Funktion; ohne Funktionsprototyp wären hier
// Argumenttyp (int) und Parametertyp (double) inkompatibel:
printf("2 + 3 = %g\n", summe(2, 3));
return 0;
}
// Definition der Funktion:
double summe(double zahl1, double zahl2) {
return zahl1 + zahl2;
}
Zeiger
Grundsätzliches
- Adresse + Typ eines Objekts
- Zeiger referenziert (zeigt auf) Adresse
- Objekttyp gibt Größe der Speicherzelle an
- Deklaration: Datentyp *name;
- z.B.:
- int *p (Datentyp ist hier int *, also die Adresses eines int Wertes)
- &p liefert Adressse von p
- Bsp.:
int *ptr; // Zeiger auf int
int value = 123; // eine int-Variable
ptr = &value; // der Zeiger ptr zeigt auf value
Call-by-Reference
- Normalerweise wird in C eine Kopie der Variable übergeben
- Änderungen von der Variable haben keine Auswirkung außerhalb der Funktion
- Wird aber ein Zeiger auf die Variable übergeben, so ändert sich die Variablen
- Bsp.:
int main (){
int x = 2;
int y = 3;
swap (&x, &y);
}
void swap (int *i1, int *i2){
int help;
help = *i1;
*i1 = *i2;
*i2 = help;
}
NULL-Zeiger
- Um Segmentation fault zu vermeiden Zeiger mit NULL initialisieren
- int *iptr = NULL
Zeiger und Arrays
- int a[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
- a zeigt auf 1. Array Element a[0]
int *pa;
pa = a;
- pa zeigt auf a[0]
- pa+1 und a zeigen auf a[1]
- Bsp.:
int main () {
int a[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
int *pa;
pa = a;
for (i = 0; i<4; i++)
printf ("Adresse: %p, Wert: %2d\n", pa+i, *(pa+i));
return 0;
}
Structs
- Bsp.:
struct Books {
char title[50];
char author[50];
char subject[100];
int book_id;
};
int main( ) {
struct Books Book1; /* Declare Book1 of type Book */
struct Books Book2; /* Declare Book2 of type Book */
/* book 1 specification */
strcpy( Book1.title, "C Programming");
strcpy( Book1.author, "Nuha Ali");
strcpy( Book1.subject, "C Programming Tutorial");
Book1.book_id = 6495407;
/* book 2 specification */
strcpy( Book2.title, "Telecom Billing");
strcpy( Book2.author, "Zara Ali");
strcpy( Book2.subject, "Telecom Billing Tutorial");
Book2.book_id = 6495700;
/* print Book1 info */
printf( "Book 1 title : %s\n", Book1.title);
printf( "Book 1 author : %s\n", Book1.author);
printf( "Book 1 subject : %s\n", Book1.subject);
printf( "Book 1 book_id : %d\n", Book1.book_id);
/* print Book2 info */
printf( "Book 2 title : %s\n", Book2.title);
printf( "Book 2 author : %s\n", Book2.author);
printf( "Book 2 subject : %s\n", Book2.subject);
printf( "Book 2 book_id : %d\n", Book2.book_id);
return 0;
}
typdef struct
- Bei Verwendung von typdef kann bei der Deklarierung das Schlüsselwort “struct” weggelassen werden
- Bsp.:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
//normal structure declaration
struct student_str {
char name[30];
int age;
};
//structur declaration with typedef
typedef struct {
char name[30];
int age;
}employee_str;
//main code
int main()
{
//declare structure variable for student_str
struct student_str std;
//declare structure variable for employee_str
employee_str emp;
//assign values to std
strcpy(std.name, "Amit Shukla");
std.age = 21;
//assign values to emp
strcpy(emp.name, "Abhishek Jain");
emp.age = 27;
//print std and emp structure
printf("Student detail:\n");
printf("Name: %s\n",std.name);
printf("Age: %d\n",std.age);
printf("Employee detail:\n");
printf("Name: %s\n",emp.name);
printf("Age: %d\n",emp.age);
return 0;
}